
HTRF Human and Mouse Phospho-NPM1 Thr199 Detection Kit, 10,000 assay points
HTRF Human and Mouse Phospho-NPM1 Thr199 Detection Kit, 10,000 assay points


This HTRF kit allows for the cell-based quantitative detection of NPM1 when phosphorylated at Thr199.
| Feature | Specification |
|---|---|
| Application | Cell Signaling |
| Sample Volume | 16 µL |
This HTRF kit allows for the cell-based quantitative detection of NPM1 when phosphorylated at Thr199.


HTRF Human and Mouse Phospho-NPM1 Thr199 Detection Kit, 10,000 assay points


HTRF Human and Mouse Phospho-NPM1 Thr199 Detection Kit, 10,000 assay points


Product information
Overview
NPM1 (Nucleophosmin 1) is a molecular chaperone involved in cell cycle regulation, ribosome biogenesis, cell proliferation, DNA damage repair, and apoptosis. Its phosphorylation on Thr199 by the CDK2/Cyclin E complex regulates mitosis, centrosome duplication, pre-mRNA processing, and G2/M cell cycle arrest through its interaction with p53/MDM2.
NPM1 functions both as an oncogene and a tumor suppressor. It is frequently overexpressed, altered, and rearranged, or sporadically deleted in human cancers. NPM1 is also the most frequently mutated gene (NPM1c) in acute myeloid leukemia (AML).
Specifications
| Application |
Cell Signaling
|
|---|---|
| Automation Compatible |
Yes
|
| Brand |
HTRF
|
| Detection Modality |
HTRF
|
| Lysis Buffer Compatibility |
Lysis Buffer 4
|
| Molecular Modification |
Phosphorylation
|
| Product Group |
Kit
|
| Sample Volume |
16 µL
|
| Shipping Conditions |
Shipped in Dry Ice
|
| Target |
NPM1
|
| Target Class |
Phosphoproteins
|
| Target Species |
Human
Mouse
|
| Technology |
TR-FRET
|
| Therapeutic Area |
Oncology
|
| Unit Size |
10,000 assay points
|
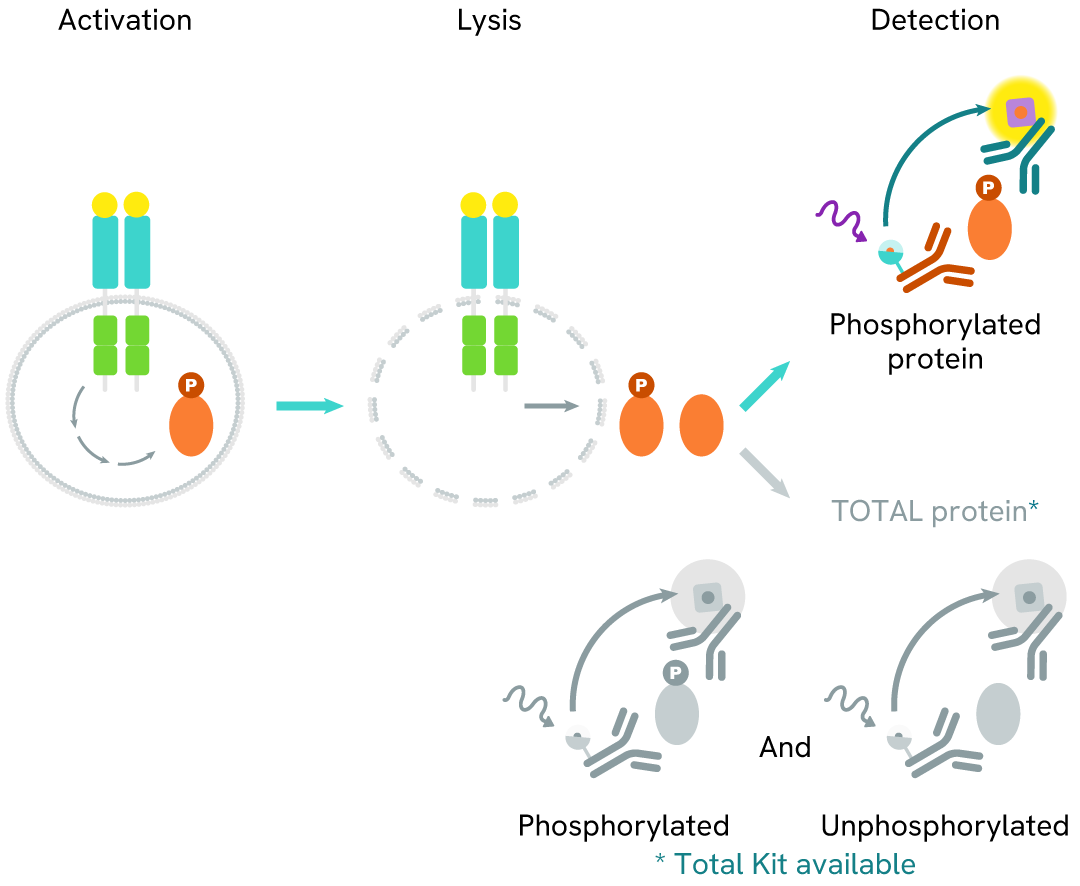
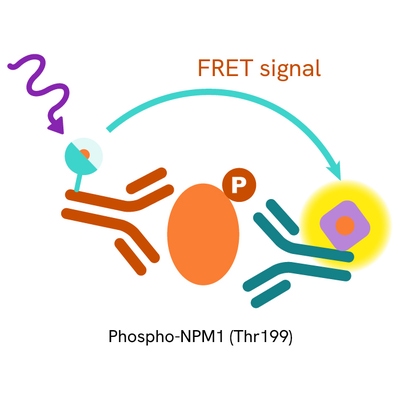
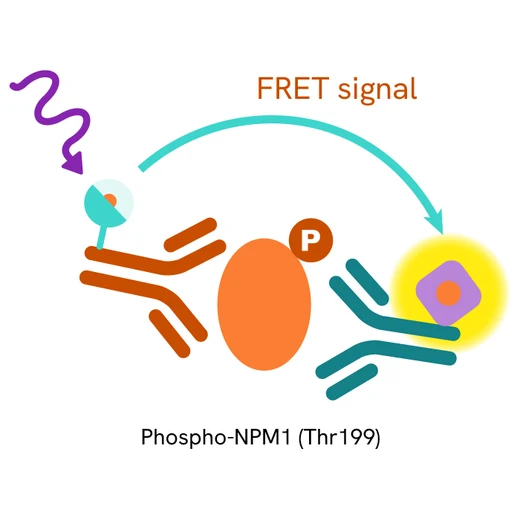
How it works
Phospho-NPM1 (Thr199) assay principle
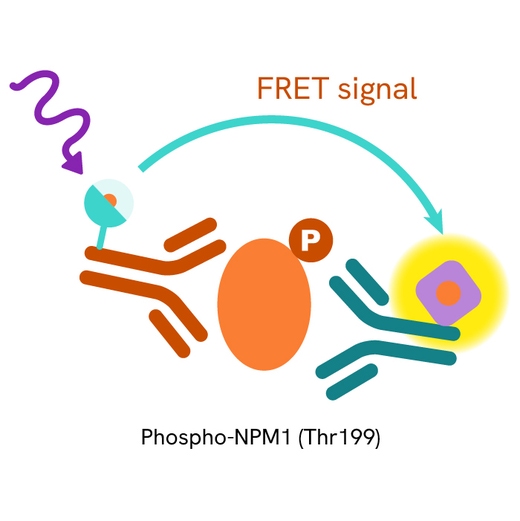
The Phospho-NPM1 (Thr199) assay measures NPM1 when phosphorylated at Thr199. Unlike Western Blot, the assay is entirely plate-based and does not require gels, electrophoresis, or transfer. The assay uses 2 antibodies, one labeled with a donor fluorophore and the other with an acceptor. The first antibody was selected for its specific binding to the phosphorylated motif on the protein, and the second for its ability to recognize the protein independently of its phosphorylation state. Protein phosphorylation leads to an immune-complex formation involving both labeled antibodies, and which brings the donor fluorophore into close proximity to the acceptor, thereby generating a FRET signal. Its intensity is directly proportional to the concentration of phosphorylated protein present in the sample and provides a means of assessing the protein's phosphorylation state under a no-wash assay format.

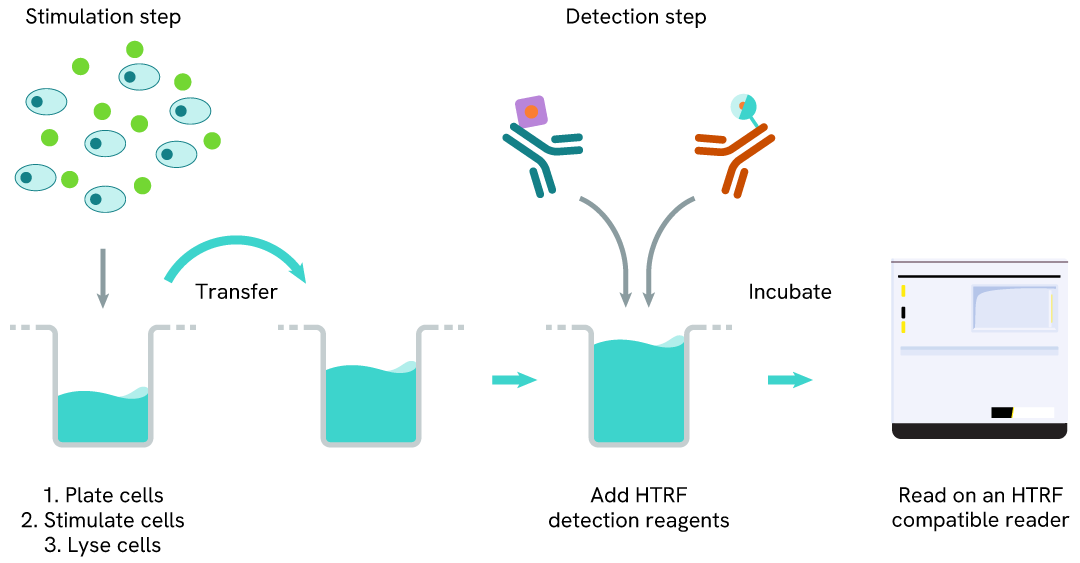
Phospho-NPM1 (Thr199) two-plate assay protocol
The two-plate protocol involves culturing cells in a 96-well plate before lysis, then transferring lysates into a 384-well low volume detection plate before the addition of Phospho-NPM1 (Thr199) HTRF detection reagents. This protocol enables the cells' viability and confluence to be monitored.
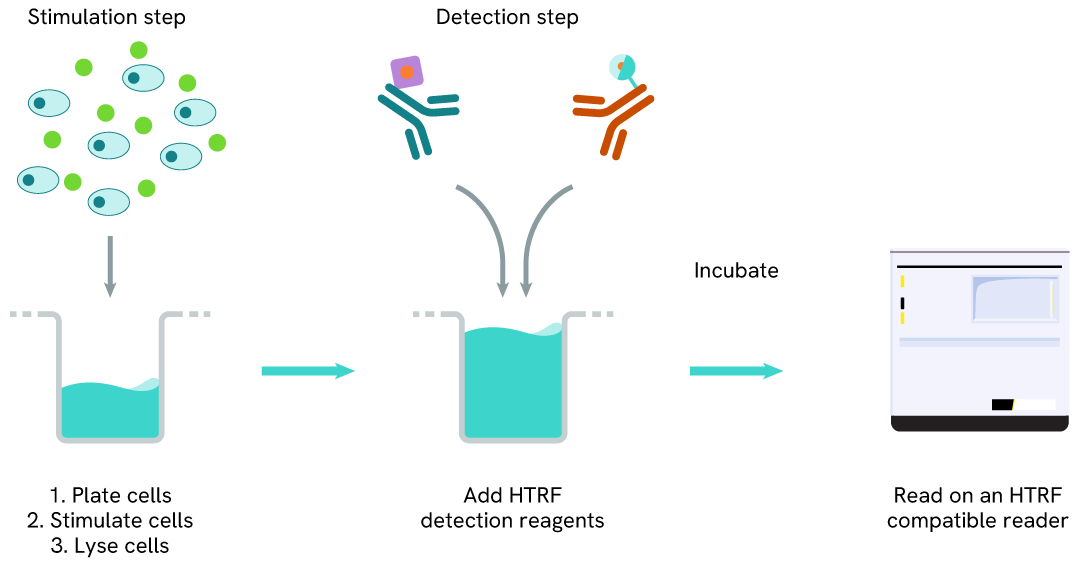
Phospho-NPM1 (Thr199) one-plate assay protocol
Detection of Phosphorylated NPM1 (Thr199) with HTRF reagents can be performed in a single plate used for culturing, stimulation, and lysis. No washing steps are required. This HTS designed protocol allows miniaturization while maintaining robust HTRF quality.
Assay validation
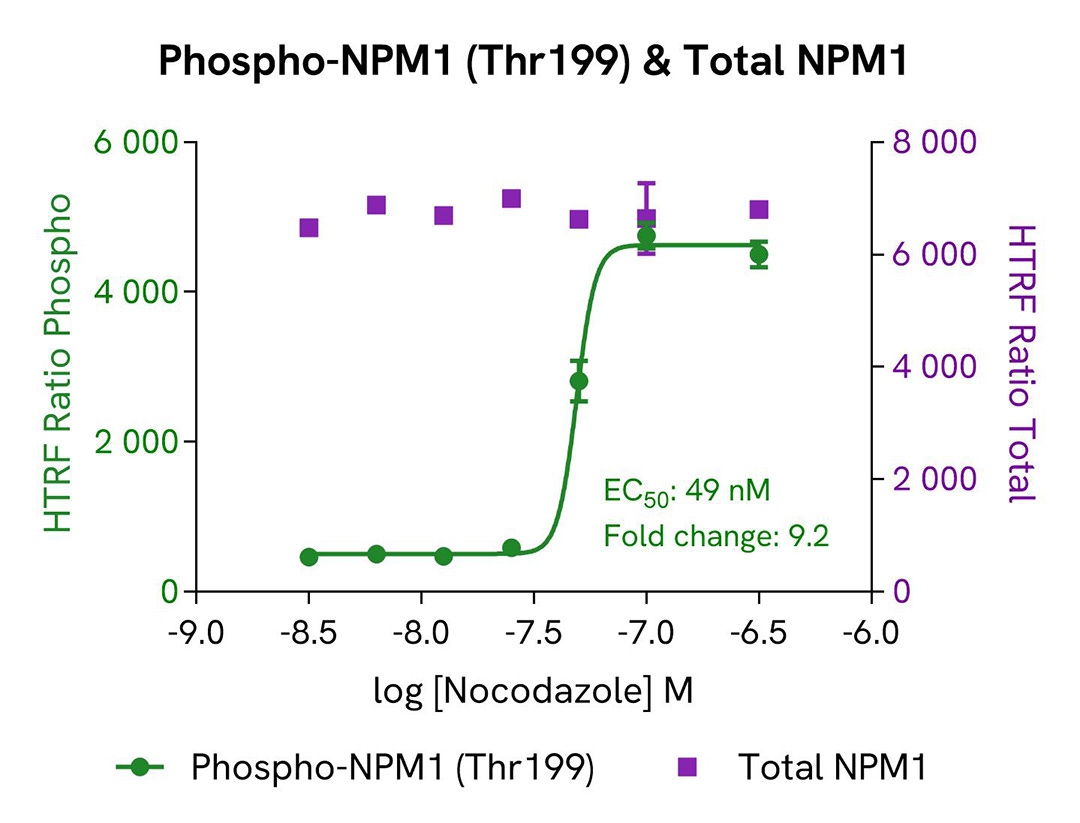
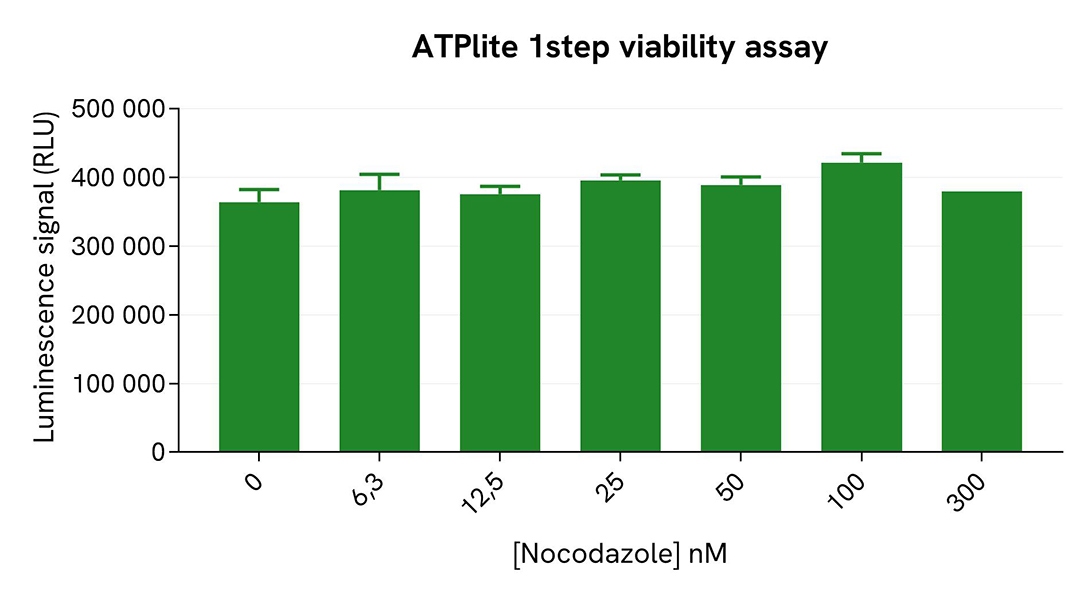
Induction of phospho-NPM1 (Thr199) by Nocodazole
The human breast cancer cell line MCF-7 was seeded in a 96-well culture plate (25,000 cells/well) in complete culture medium, and incubated for 5 hours at 37°C, 5% CO2. The cells were then treated for 18 hours with increasing concentrations of Nocodazole.
After treatment, the cells were lysed with 50 µL of supplemented lysis buffer #4 for 30 minutes at RT under gentle shaking. For the detection step, 16 µL of lysate were transferred into a 384-well low volume white microplate (ProxiPlate-384 Plus, Cat # 6008280/9), and 4 µL of the HTRF Phospho-NPM1 (Thr199) or Total NPM1 detection reagents were added (lysates diluted 4-fold in supplemented lysis buffer before detection of Total NPM1). After a 3h-incubation step at RT, the HTRF signal was recorded on an EnVision Nexus reader. Cell viability was also assessed by transferring 5 µL of the same lysate into an HTRF 96-well low volume white plate (Cat # 66PL96005/025/100), followed by the addition of 25 µL of ATPlite 1step reagent (ATPlite 1step Luminescence Assay System, Cat # 6016736/1/9). The luminescence signal was measured on an EnVision Nexus reader after a 10-min incubation at RT in the dark.
As expected, the cell cycle blocker Nocodazole (which induces cell cycle arrest at G2/M phase) triggered a dose-dependent increase in the level of Phospho-NPM1 (Thr199), while the expression level of NPM1 and the cell viability remained stable.
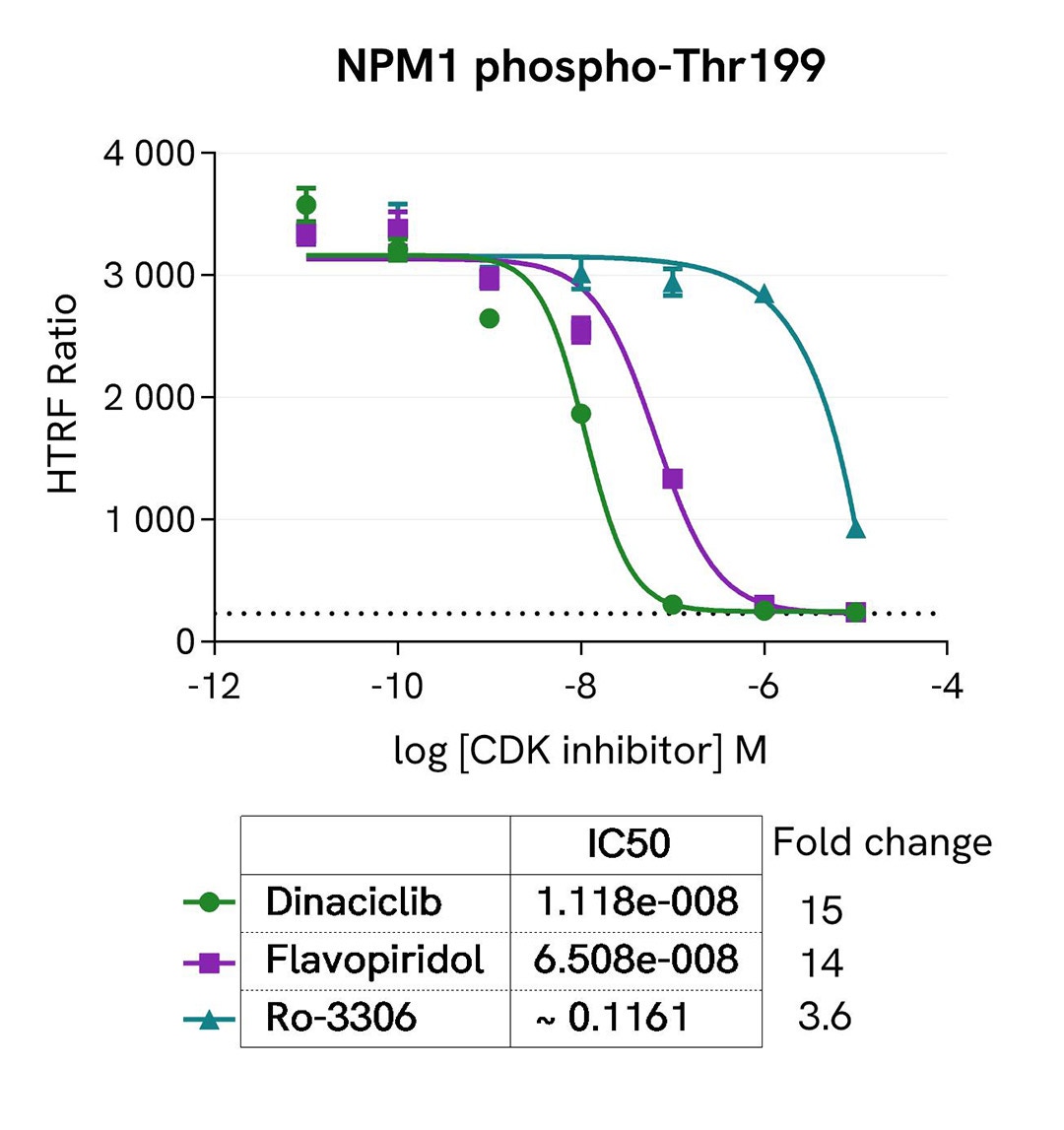
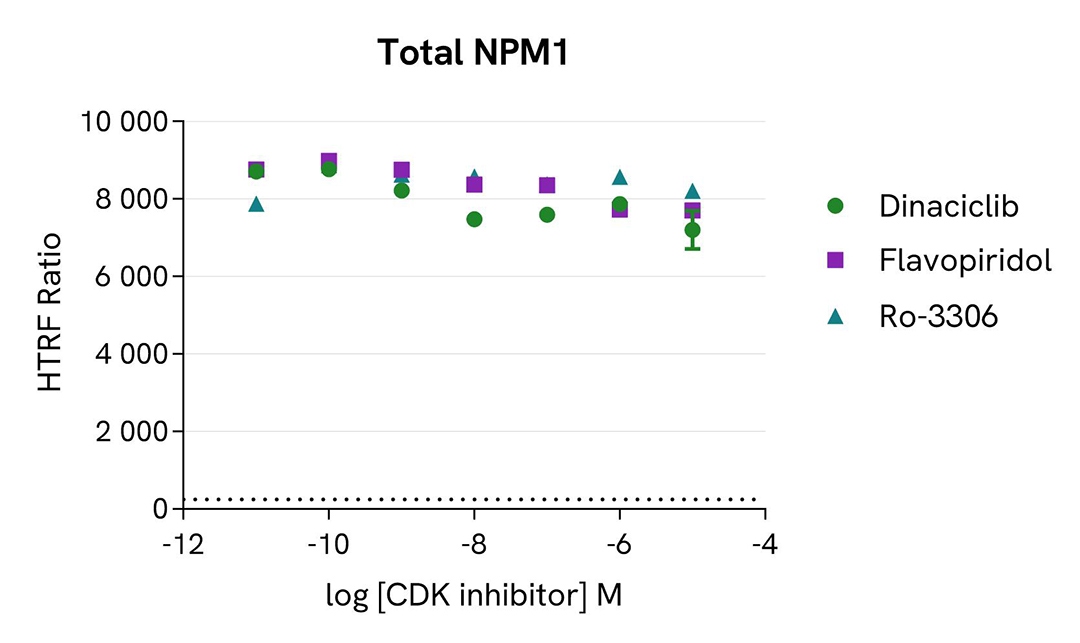
Inhibition of phospho-NPM1 (Thr199) by CDK inhibitors
MCF-7 cells were seeded in a 96-well culture plate (25,000 cells/well in complete culture medium) and incubated for 5 hours at 37°C, 5% CO2. The cells were treated for 1 hour with increasing concentrations of the CDK inhibitors Dinaciclib, Flavopiridol hydrochloride, and Ro-3306, and then incubated overnight with 100 nM Nocodazole. The cells were lysed with 50 µL of supplemented lysis buffer #4 for 30 minutes at RT under gentle shaking.
For the detection step, 16 µL of lysates (previously diluted 4-fold in supplemented lysis buffer) were used to detect Phospho-NPM1 (Thr199) or Total NPM1 using the HTRF kits, and 5 µL of the same lysate were used to assess cell viability using the ATPlite 1step Luminescence Assay System, as described in the previous section.
As expected, the three inhibitors induced a dose-dependent decrease in NPM1 phosphorylation at Thr199, and showed different potencies correlated with the literature. The expression level of NPM1 as well as cell viability monitored with the ATPlite 1step assay (data not shown here) were not affected by the treatment with the inhibitors.
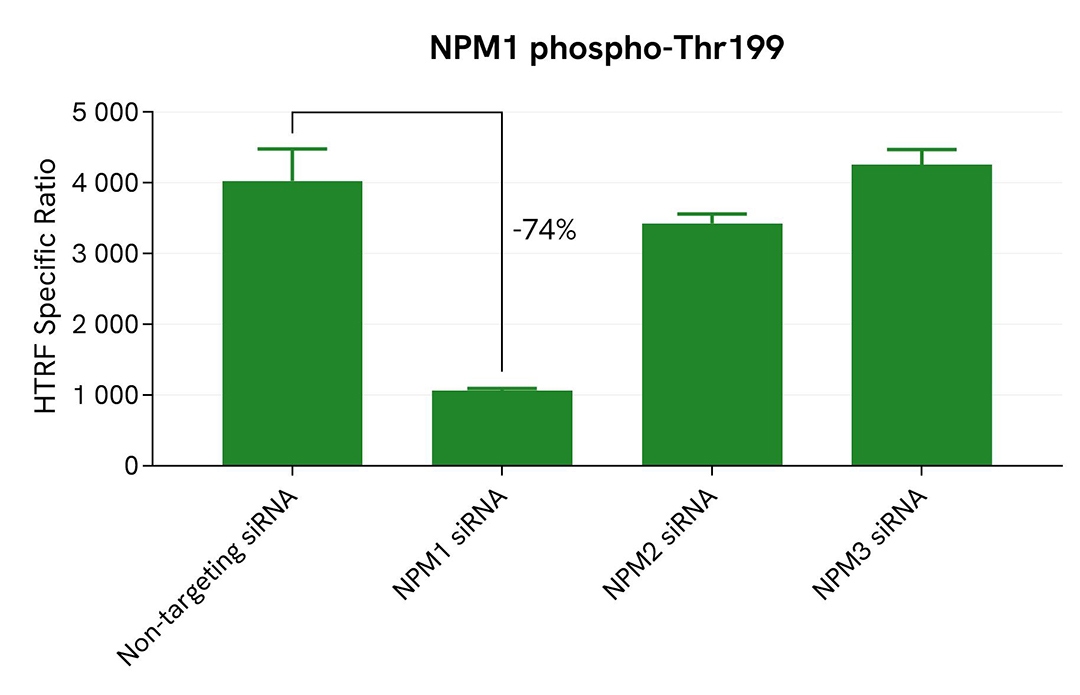
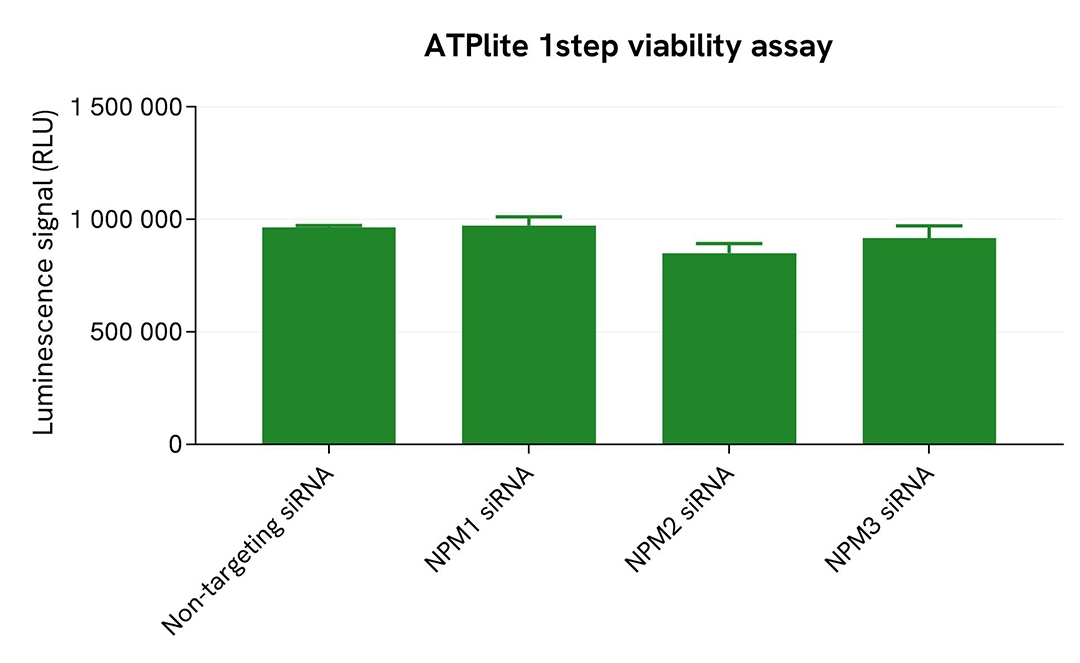
Validation of phospho-NPM1 (Thr199) assay specificity by siRNA experiments
HepG2 cells were plated in a 96-well culture plate (25,000 cells/well in complete culture medium) and cultured overnight at 37°C, 5% CO2. The next day, the cells were transfected with ON-TARGETplus SMARTpool siRNAs (Horizon Discovery/Revvity) targeting human NPM1, human NPM2, or human NPM3, as well as with a non-targeting siRNA used as negative control. After a 24h incubation, the medium was renewed and supplemented with 300 nM Nocodazole for an additional 18h-incubation. The cells were lysed with 50 µL of supplemented lysis buffer #4 for 30 minutes at RT under gentle shaking. >p>For the detection step, 16 µL of lysates (previously diluted 16-fold in supplemented lysis buffer) were used to detect Phospho-NPM1 (Thr199) using the HTRF kit, and 5 µL of the same lysate were used to assess cell viability using the ATPlite 1step Luminescence Assay System, as described in the previous section.
The siRNA experiments demonstrated that the HTRF detection antibodies specifically measured Phospho-NPM1 and did not recognize the other family members. It was found that treatment with the NPM1 siRNA induced a 74% signal decrease, while the knockdown of NPM2 and NPM3 genes did not lead to any significant signal modulation in this assay. The ATPlite luminescence signal was unchanged in presence of siRNAs, demonstrating that the HTRF signal decrease was unrelated to cytotoxic effects.
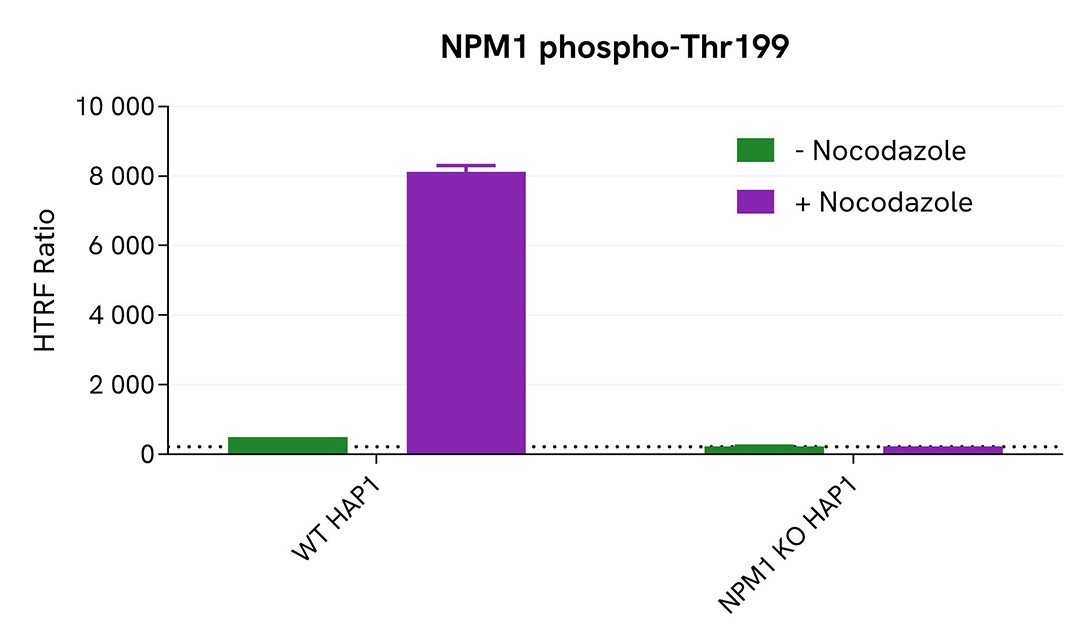
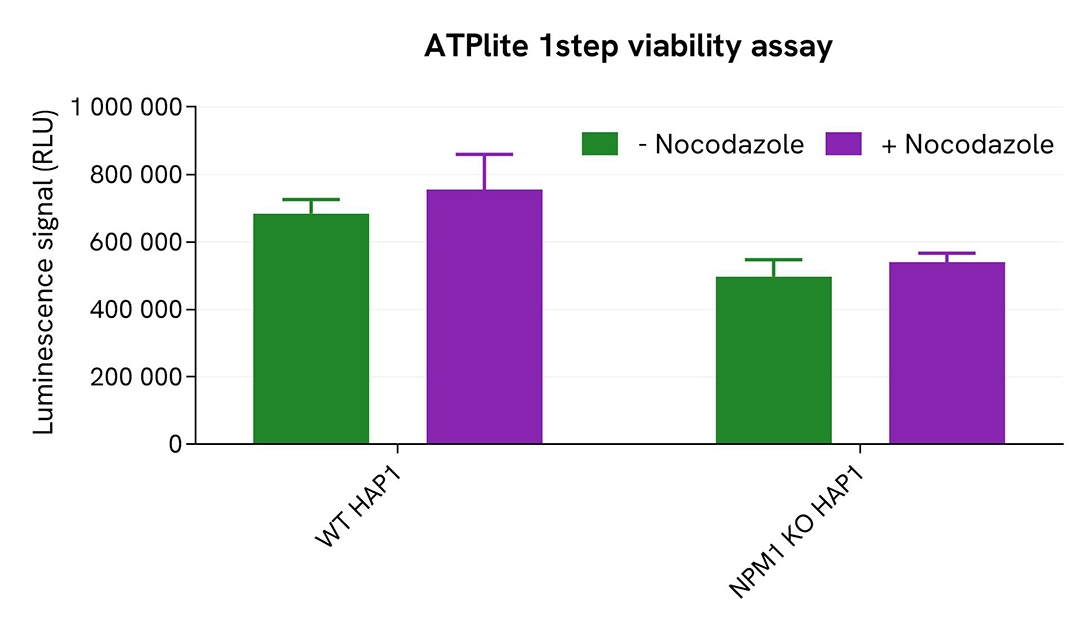
Validation of phospho-NPM1 (Thr199) assay specificity with NPM1 KO cells
The parental (WT) HAP1 cell line and the NPM1 KO HAP1 cell line (Horizon Discovery/Revvity) were seeded in a 96-well culture plate (50,000 cells/well) in complete culture medium, and incubated for 5 hours at 37°C, 5% CO2. The cells were treated or not with 200 nM Nocodazole for 18 hours, and then lysed with 50 µL of supplemented lysis buffer #4 for 30 minutes at RT under gentle shaking.
For the detection step, 16 µL of lysates (previously diluted 8-fold in supplemented lysis buffer) were used to detect Phospho-NPM1 (Thr199) using the HTRF kit, and 5 µL of the same lysate were used to assess cell viability using the ATPlite 1step Luminescence Assay System, as described in the previous section. Phospho-NPM1 (Thr199) was clearly detected in WT HAP1 cells treated with Nocodazole, while no HTRF signal was detected in NPM1 KO HAP1 cells, confirming the kit's specificity for detecting NPM1. These results were further supported by the ATPlite 1step viability assay, which confirmed the proper plating of cells and demonstrated that the treatment with Nocodazole did not induce any cytotoxic effect.
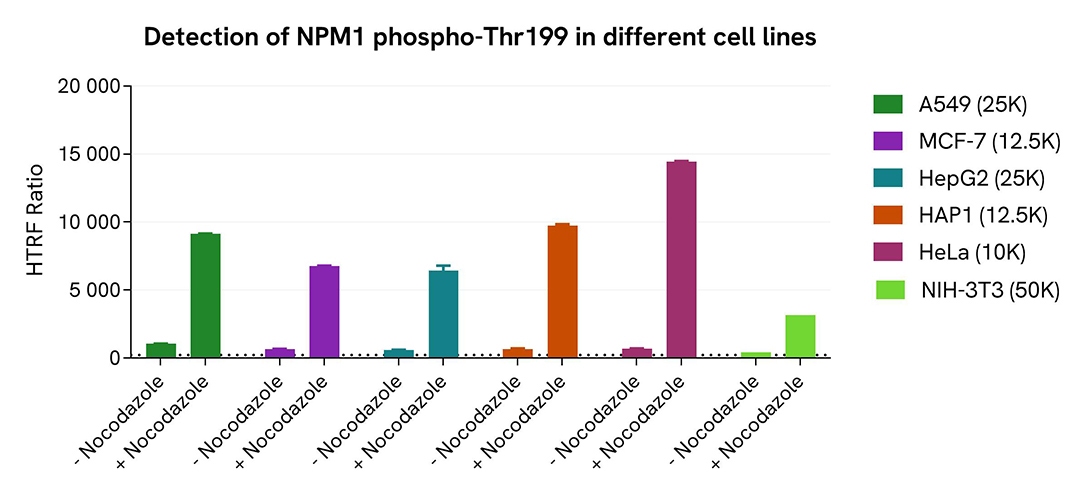
Validation of Phospho-NPM1 (Thr199) assay on different human and mouse cell lines
The human cancer cell lines A549, MCF-7, HepG2, HAP1, and HeLa, as well as the mouse fibroblastic cell line NIH-3T3, were seeded in a 96-well culture plate in complete culture medium and incubated for 5 hours at 37°C, 5% CO2. The cells were treated or not with 200 nM Nocodazole for 18 hours, and then lysed with 50 µL of supplemented lysis buffer #4 for 30 minutes at RT under gentle shaking.
For the detection step, 16 µL of lysates were used to detect Phospho-NPM1 (Thr199) using the HTRF kit, as described in the previous section.
The HTRF Phospho-NPM1 (Thr199) assay efficiently detected NPM1 phosphorylation at T199 in various human and mouse cell lines treated with Nocodazole.
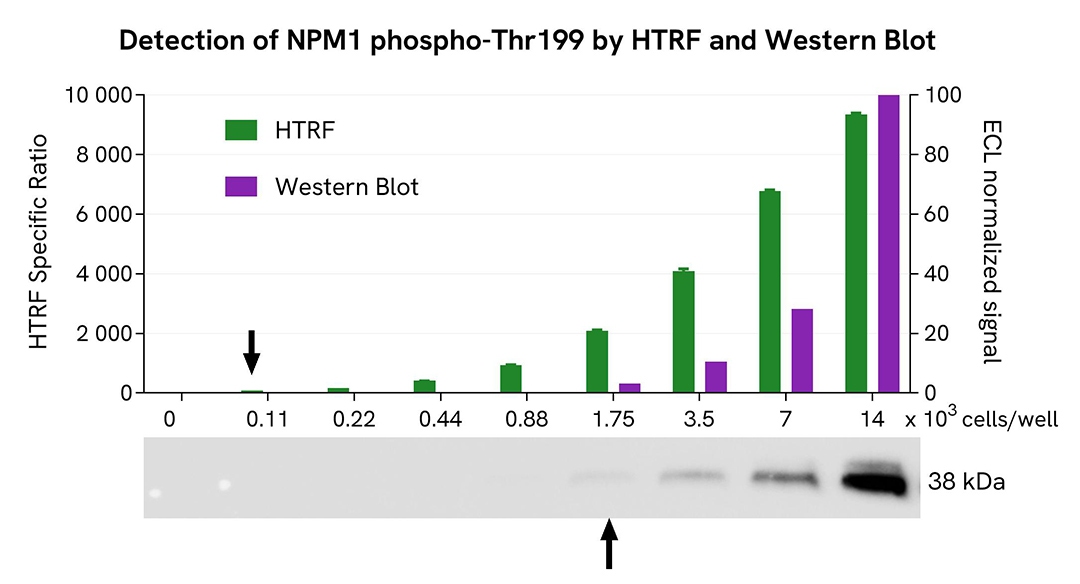
HTRF Phospho-NPM1 (Thr199) assay compared to Western Blot
HeLa cells were grown in a T175 flask in complete culture medium at 37°C, 5% CO2 until ~80% confluency was reached. The cells were treated with 300 nM Nocodazole for 20 hours and then lysed with 3 mL of supplemented lysis buffer #4 for 30 minutes at RT under gentle shaking.
Serial dilutions of the cell lysate were performed using supplemented lysis buffer, and 16 µL of each dilution were transferred into a 384-well low volume white microplate before the addition of 4 µL of the HTRF Phospho-NPM1 (Thr199) detection reagents. Equal amounts of lysates were used for a side-by-side comparison between HTRF and Western Blot.
Using the HTRF Phospho-NPM1 (Thr199) assay, 110 cells/well were enough to detect a significant signal, while 1750 cells were needed to obtain a minimal chemiluminescent signal using Western Blot. Therefore, in these conditions, the HTRF Phospho-NPM1 (Thr199) assay was 16 times more sensitive than the Western Blot technique.
Simplified pathway
NPM1 signaling pathway
Nucleophosmin 1 (NPM1) is a member of the nucleophosmin family, which also includes NPM2 and NPM3. This molecular chaperone, which has both nucleic acid and protein chaperone activity, shuttles rapidly between the nucleus and cytoplasm but predominantly resides in the nucleus.
NPM1 is a multifunctional phosphoprotein involved in diverse biological processes, such as cell cycle regulation, ribosome biogenesis, cell proliferation, DNA damage repair, and apoptosis. NPM1 plays a key role in response to various nucleolar stress stimuli, including hypoxia, heat shock, oxidative stress, UV irradiation, chemotherapy, and gamma irradiation.
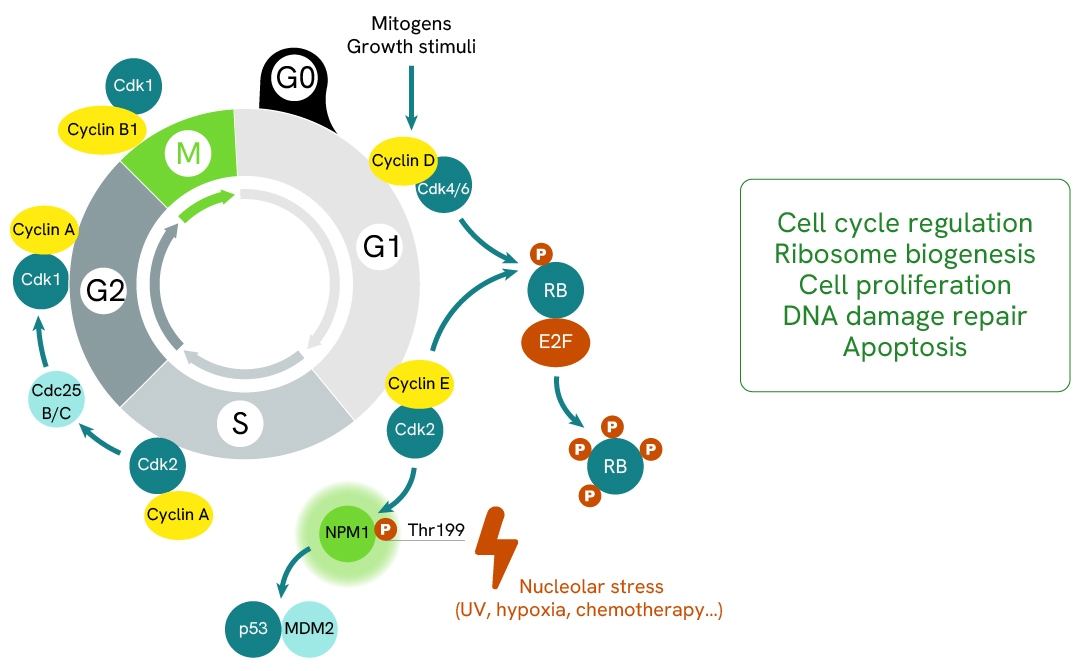
NPM1 is phosphorylated on several residues by different kinases, including CK2, PLK2, CDK1, and CDK2. The phosphorylation of Thr199 by the CDK2/Cyclin E complex regulates mitosis, is responsible for centrosome duplication and pre-mRNA processing, and reduces the ability of NPM1 to bind RNA. Additionally, Thr199 phosphorylation is required for the regulation of G2/M cell cycle arrest through its interaction with p53/MDM2.
NPM1 functions both as an oncogene and a tumor suppressor. It is frequently overexpressed, altered, and rearranged, or sporadically deleted in human cancers. NPM1 is also the most frequently mutated gene (NPM1c) in acute myeloid leukemia (AML).
SDS, COAs, Manuals and more
Are you looking for technical documents related to the product? We have categorized them in dedicated sections below. Explore now.
- Resource TypeManualLanguage英语Country-


How can we help you?
We are here to answer your questions.